Đối với bất kỳ nhà vệ sinh nào, đường ống dẫn thoát nước luôn rất quan trọng. Để hệ thống dẫn thoát nước hoạt động trơn tru thì trong thời gian xây dựng cần tuân thủ theo những tiêu chuẩn nhất định để đảm báo chất lượng cũng và tính bền bỉ theo thời gian. Tuy nhiên không phải gia chủ nào khi xây dựng cũng rõ điều này. Vậy nên thông tắc cống 24h chúng tôi xin chia sẻ kinh nghiệm cách đi đường nước nhà vệ sinh sao cho hợp lý qua bài viết dưới đây.

Các tiêu chuẩn trong hệ thống dẫn thoát nước nhà vệ sinh
- Đường ống nước phải dễ dàng thi công, lắp đặt và bảo trì.
- Thiết kê đường ống nước ngắn nhất có thể.
- Cần đánh dấu hoặc có sơ đồ rõ ràng để khi có trục trặc. Ta có thể phân biệt được các đường ống nước thải một cách rõ ràng.
- Tách biệt hệ thống thoát nước của nhà vệ sinh (bồn cầu, bồn tiểu) và hệ thống thoát nước rửa (bồn tắm, sàn, lavabo).
Tham khảo thêm: Cách thong tac chau rua bat tại nhà
Đi đường nước nhà vệ sinh cần chú ý
Thiết kế hệ thống thoát nước thải
Không nên thiết kế đường ống thoát nước thải có quá nhiều đoạn chuyển hướng. Điều nay sẽ làm tăng trở lực của toàn bộ hệ thống. Khiến chất thải dễ bị đóng cặn tại các đoạn chuyển hướng. Về lâu về dài, hiện tượng tắc ứ đường ống tất yếu sẽ xảy ra.
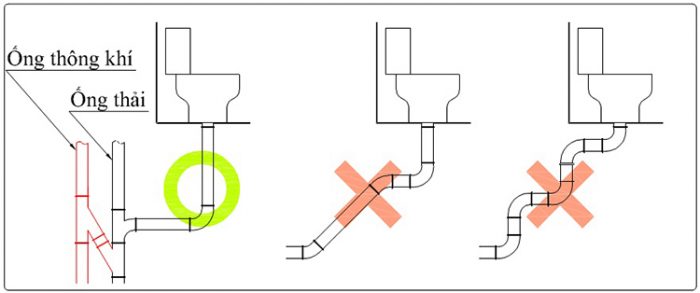
Đường ống thải nhất định phải có ống khí. Điều này sẽ giúp lực xả nước mạnh hơn cũng như tránh các việc áp lực khí nén trong đường ống quá mạnh làm vỡ ống.
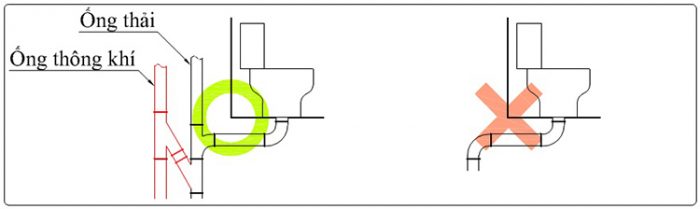
Lắp đặt đường ống thoát ngang
Lắp đặt các loại đường ống thoát ngang thì yếu tố chú ý đầu tiên sẽ phải cần đảm bảo độ nghiêng của ống thải so với thiết bị. Nếu không có độ dốc xuống của đường ống sẽ gây ảnh hưởng đến hiệu quả xả. Ngoài việc chất thải không được xả triệt để ra cũng có thể xảy ra tình trạng nước bẩn tràn ngược vào thiết bị.
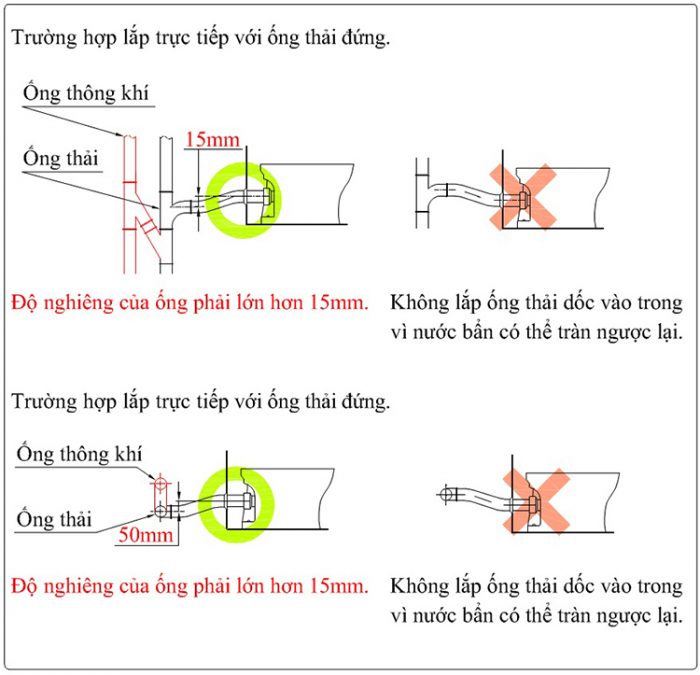
Sử dụng co nối
Cần phải hạn chế tối đa các đoạn nối. Do điều này cũng trực tiếp tạo ra trở lực, làm chất thải vận chuyển trong đường ống ứ đọng.
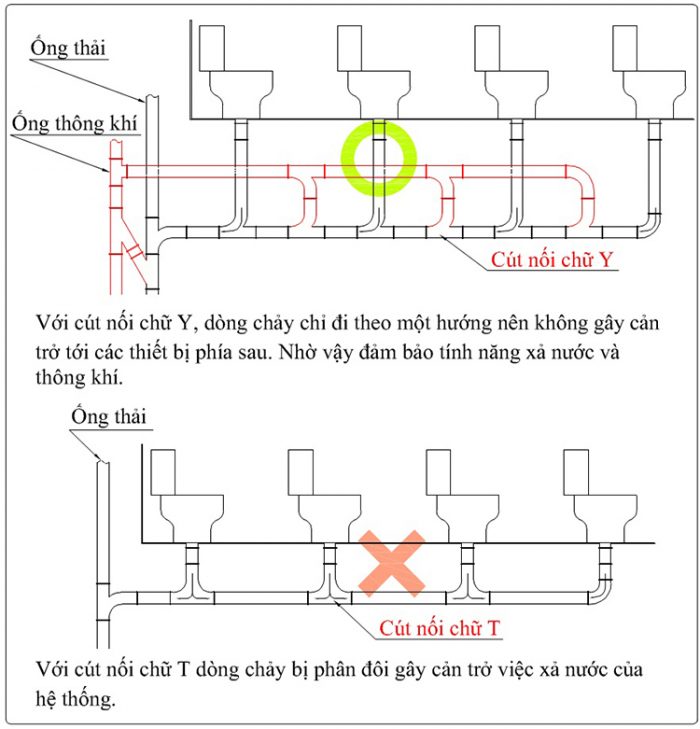
Khi lắp đặt nhiều thiết bị trên một đường ống cần sử dụng các loại cút chữ Y thay cho cút chữ T:
Với cút chữ Y dòng chảy sẽ chảy theo một hướng cho nên sẽ không cản trở tới các thiết bị sau. Đối với cút chữ T sẽ làm dòng chảy bị chia đôi gây ảnh hưởng đến quá trình xả của những thiết bị sau. Lực xả của nước cũng theo đó yếu đi.
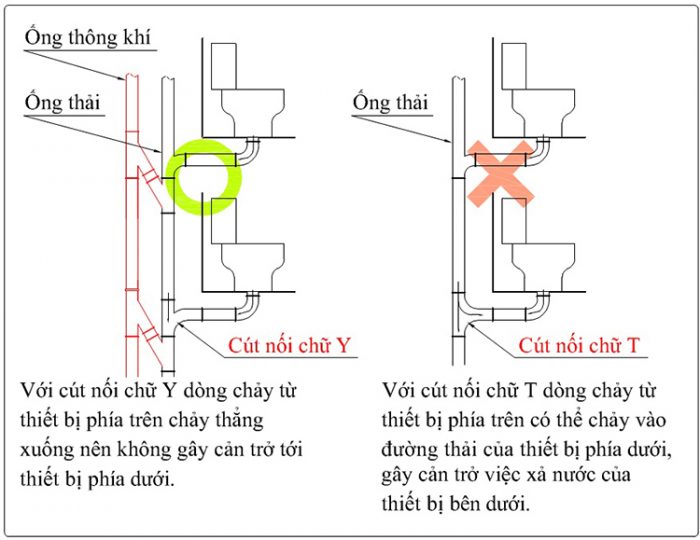
Điều này cũng đúng khi lắp các thiết bị với độ cao khác nhau. Việc nước thải chảy từ trên xuống sẽ không cản trở quá trình xả của các thiệt bị khác bên dưới. Nếu lắp các loại cút chữ T rất có thể xảy ra tình trạng nước thải tràn vào đường ống các thiết bị khác.
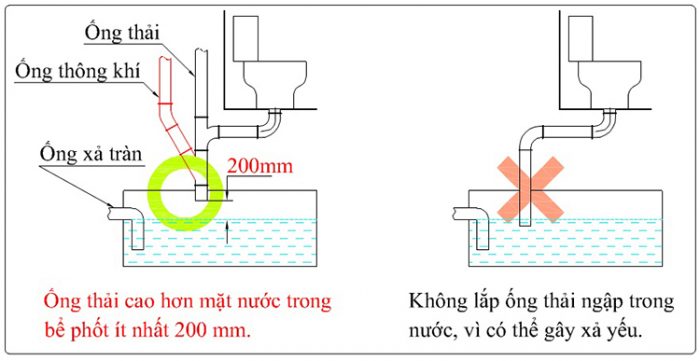
Đặt ống nước thải xuống bồn cầu
Khi đặt ống nước thải xuống bể phốt không được để bị ngập nước. cần phải đặt cao hơn mặt nước ít nhất 200mm để đảm bảo hệ thống xả tốt nhất.
Các sơ đồ đường nước trong nhà phổ biến hiện nay

Sơ đồ hệ thống đường ống cung cấp nước sinh hoạt trong nhà
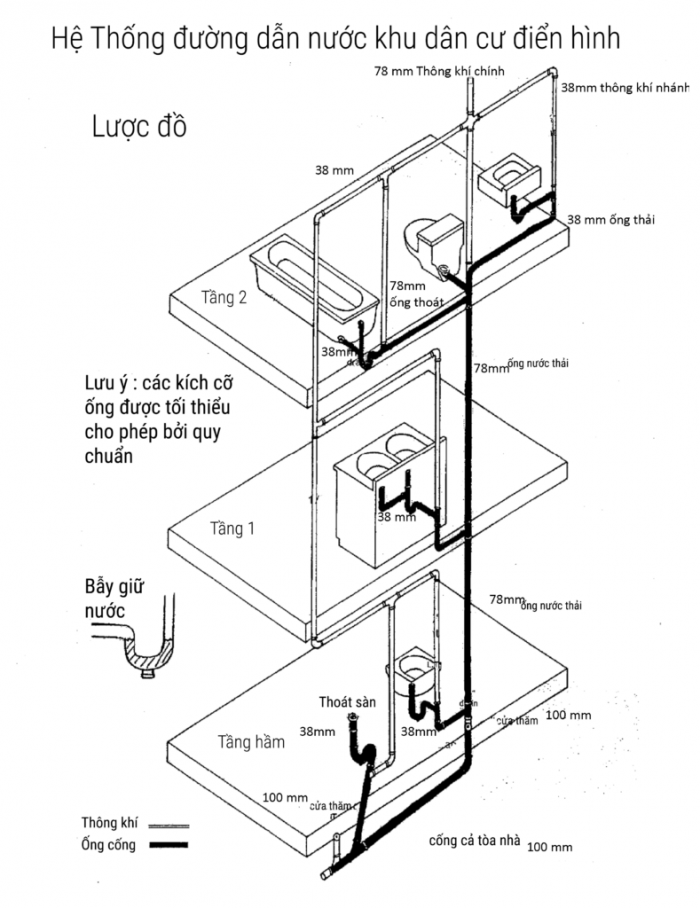
Sơ đồ đường cấp nước cơ bản khu dân cư điển hình
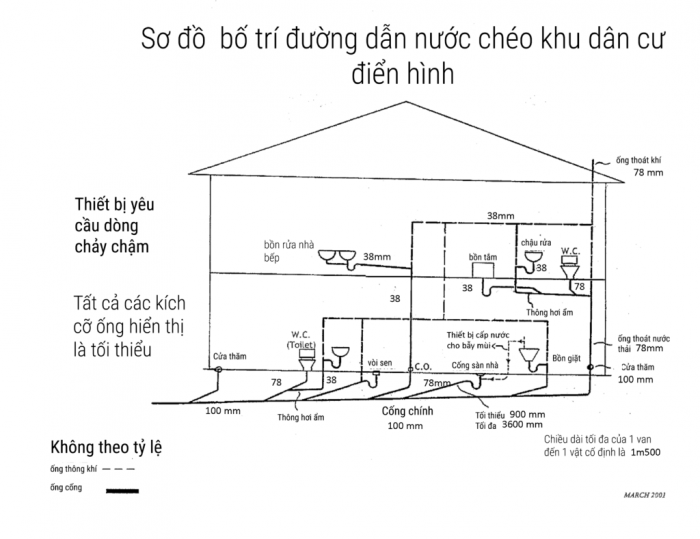
Sơ đồ đường cấp nước chéo khu dân cư điển hình
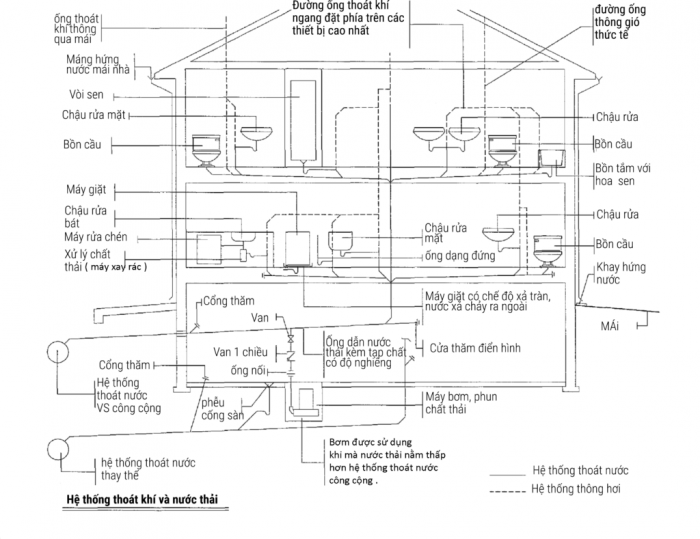
Sơ đồ hệ thống đường ống cung cấp nước sinh hoạt trong nhà
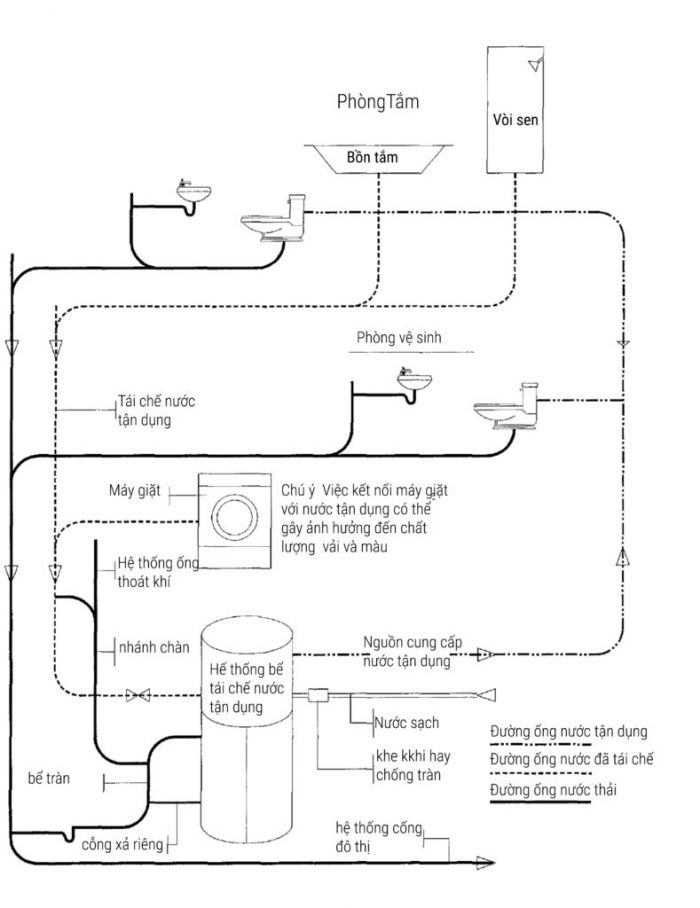
Sơ đồ hệ thống cấp thoát nước nước tái sử dụng cho nhà dân dụng